Increased uric acid accumulates in the blood. This hyperuricemia is normally asymptomatic.
An acute gout attack can appear over and over again in the course of disease. Great increases in uric acid concentration often cause an acute gout attack, but this is usually accompanied by a strong variation, which occurs after excessive alcohol consumption.
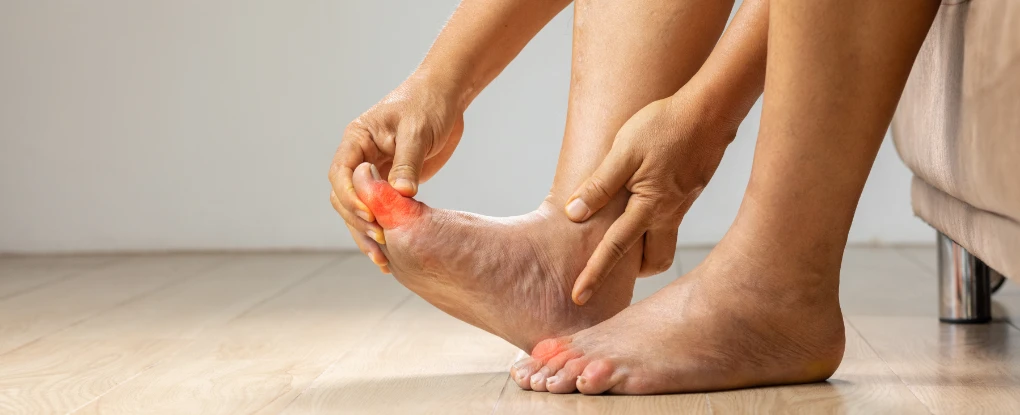
The acute gout attack is characterized by sudden joint pain, which goes along with swelling and redness of the joint. Often the affected area is also very warm. In most cases joint pain manifests on big toe joint, but also fingers, hand and knee joints can be affected by an acute gout attack. Furthermore, fever, headache and increased heart rate can appear.
After the acute gout attack the intercritical stage follows. No symptoms appear at that time -> this phase can last several months to several years
Chronic gout develops, if gout is not treated over a long time period -> characteristics are permanent joint pain and damaged articular cartilage -> So-called „gouty tophi“ are developed -> nodes up to 1cm diameter, which are shimmering whitely under the skin -> the nodes are filled with a viscous mass of uric acid, which is drained occasionally
It is important to manage gout during all stages to prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of future attacks. This includes lifestyle changes, such as a low-purine diet, weight loss and regular exercise, as well as medication to manage pain, inflammation and uric acid levels. Anyone experiencing symptoms of gout should seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.