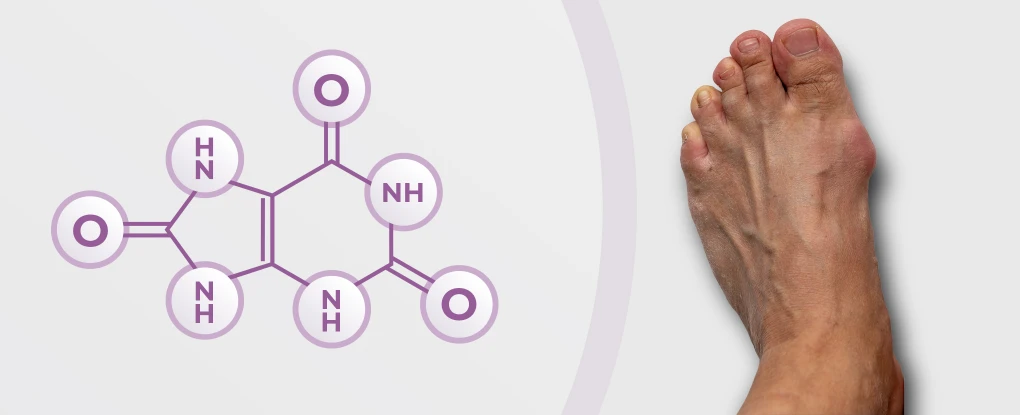
Uric acid is a chemical created when the body breaks down substances called purines. Purines are normally produced in the body and are also found in some foods and drinks. Foods with high content of purines include liver, anchovies, mackerel, dried beans and peas and beer.
Most uric acid dissolves in blood and travels to the kidneys. From there it passes out in urine. If body produces too much uric acid or does not remove enough of it, person can get sick. A high level of uric acid in the blood is called hyperuricemia.
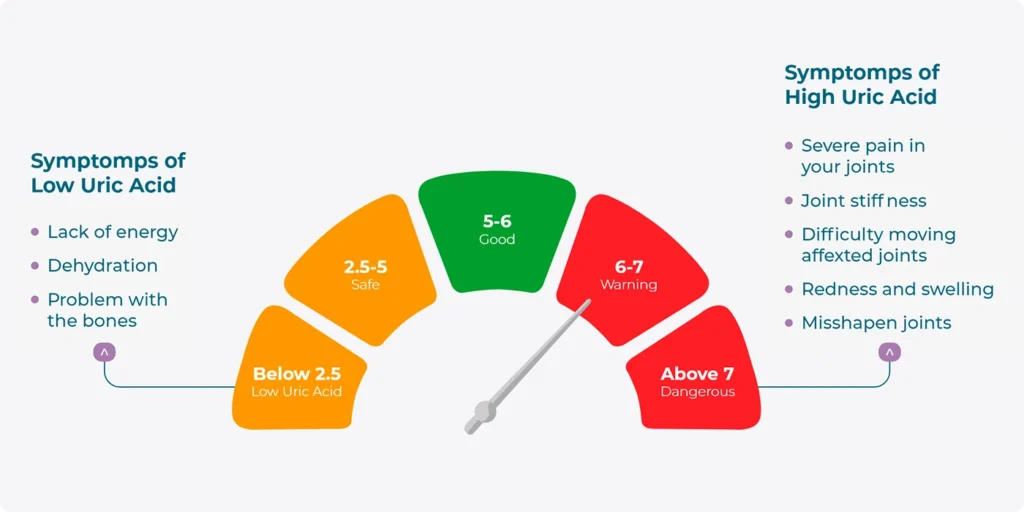
The Your patient is under the risk, if he has uric acid level more than 6 ml/dl5
When there’s an excess of uric acid in the blood, it can cause urate crystals to form. These microscopic crystals can surround joints and make them red, swollen and painful.
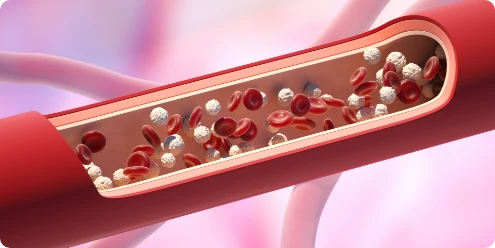
Uric acid in the blood

Uric acid crystals under microscope
Aggregates of urate crystals are known as tophi. They are microscopic at first and can exist silently for years in the setting of sustained asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Over time, they can become macroscopic and can be seen during physical exams as lumps or nodules. Uric acid can also crystallize in the renal collecting system and form calculi.
Recent meta-analysis made in 2021 of four cohort studies with a mean follow-up of 11.2 years, showed that higher SU levels at baseline were associated with an increased risk of developing gout (dose-dependent) compared with baseline SU5.
HR = Hazard ratio
SU = Serum urate
CI = Confident intervalo

How to treat
hyperuricemia?