Eating large amounts of foods high in purines including red meat, organ meat and shellfish can trigger flares
Especially beer or grain liquors, or binge drinking
This especially includes high-protein fad diets. Patient should consult a doctor before making any sudden dietary changes.
Although treating gout with uric acid-lowering medications is important for many gout sufferers and is often the best long-term solution for controlling gout starting, a new medication can trigger flares. If gout symptoms seem to be developing after starting medication, patient should call the medical professional who prescribed the medication before stopping treatment.
Radiation therapy – radiotherapy is associated with increased oxidative damage to DNA7.
DNA = Deoxyribonucleic Acid
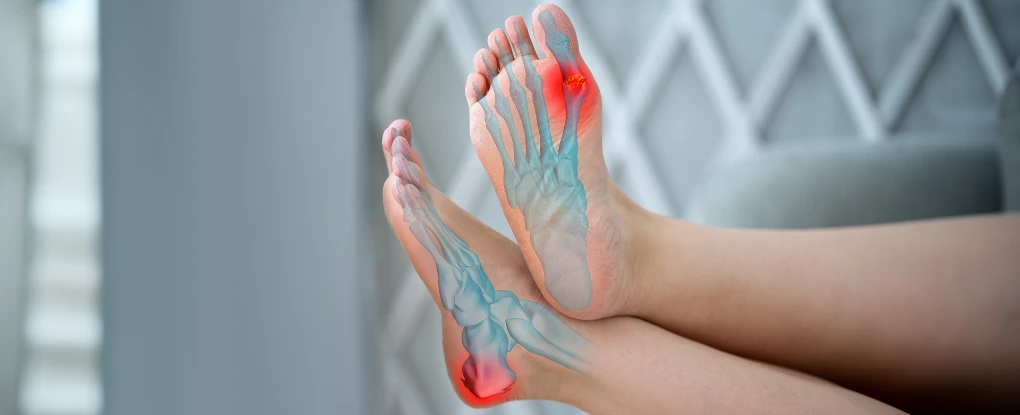
Gout arthritis is extremely painful. Patients experiencing a gout flare regularly rate their level of pain as a 9 or 10 on a standard pain scale When gout is in its intermittent stage, most flares last for 5-7 days.

High intake of purine-rich foods

Stressful life
events

Illnes or injury

Medications

Excessive
alcohol intake

Rapid weight
changes

Overeating or
fasting

Dehydration
